 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
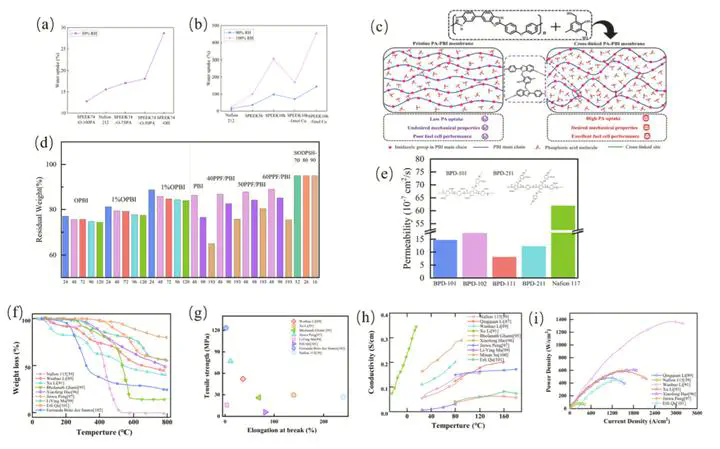
Hydrogen energy is regarded as a pivotal component in the future energy system. The PEM is a pivotal component within the hydrogen energy technology chain. Nevertheless, the elevated expense of conventional perfluorosulfonate membranes (for instance, Nafion) curtails their commercialisation. Concurrently, the sub- stantial performance deterioration of PEMs in elevated temperatures or low humidity conditions compromises the efficiency and durability of fuel cells. Moreover, chemical degradation and mechanical fatigue, attributable to the curtailment of the membrane’s lifespan, are imperative issues that necessitate prompt resolution. In order to address these challenges, significant progress has been made in recent years by both academia and industry in areas such as the development of new materials. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of PEMs and the processes involved in their preparation. A comparison of the fundamental properties of the various types of proton membranes is presented, including water absorption, swelling, oxidative stability, tensile strength and electrical conductivity. The paper also reviews state-of-the-art structural designs in monomers and polymers, taking into account the combined effects of cost, lifespan, and performance. In addition, future challenges and possibilities in the development of PEMs are thoroughly foreseen.