Substrate-dependent proton transport and nanostructural orientation of perfluorosulfonic acid polymer thin films on Pt and carbon substrate
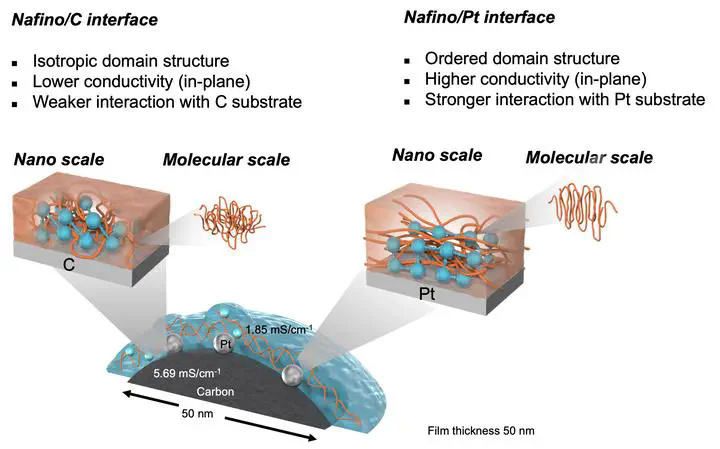 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
The electrochemical reactions occur on the carbon-supported platinum covered by a proton conducting polymer electrolyte. Thus, it is important to clarify the correlation between proton conductivity and morphology of the polymer electrolyte on Pt or carbon. In this study, the properties of thin films (50–200 nm) of Nafion®, which is the typical polymer electrolyte, were investigated on platinum and carbon substrates. Grazing-incidence small/ wide angle X-ray scattering and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were used to extract morphological and proton transport information. Self-designed interdigitated array electrodes were utilized to test and compare the proton conductivity on the Pt and carbon substrates. Based on the results, the difference in anisotropic behavior of Nafion thin films on each substrate were explored, which exhibit that the proton conductivity of Pt- supported Nafion thin films has more well defined hydrophilic domain structure than that of carbon supported thin films along in-plane direction and while it showed the opposite trend in the out-of-plane direction. These datasets and analyses represented a thorough study of the behavior of Nafion thin films on model substrates of interest, i.e., Pt catalyst/carbon electrodes. These results are expected to further understanding the difference in term of proton transport pathway.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.